orbital floor fracture complications
To provide a platform for discussion of current ideas in urologic education patient engagement. Facial fractures have been categorized according to multiple schemas most famously according to a simplified three-tier Le Fort classification for complex midface fractures.
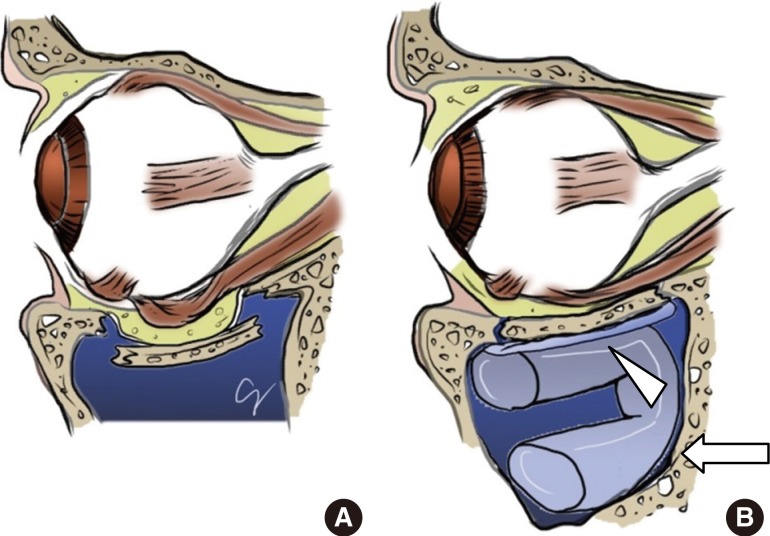
Orbital floor fractures may occur in isolation blowout fractures or as part of a zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture.

. While the diagnosis of traumatic brain injury TBI is a clinical decision neuroimaging remains vital for guiding management on the basis of identification of intracranial pathologic conditions. A break in continuity of bone. Cleft lip and palate and.
The International Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons IAOMS is the largest not-for-profit professional association representing oral and maxillofacial surgeons worldwide. The terms pure and impure have been used to describe isolated orbital fractures pure versus orbital fractures that occur in conjunction with other fractures impure 5. Orbital floor fracture blowout fracture may also occur as a result of the forceful blunt trauma to the eye.
A blowout Fracture of the orbital floor is defined as a fracture of the orbital floor in which the inferior orbital rim is intact. In these circumstances proper technique prevents intracranial placement of a nasal pack. It is estimated that about 10 of all facial fractures are isolated orbital wall fractures the majority of these being the orbital floor and that 30-40 of.
Patients less than approximately 10 years of age may need emergent surgery to release the muscle from the fracture to. The monthly publication features timely original peer-reviewed articles on the newest techniques dental materials and research findings. It may be caused by trauma twisting due to muscle spasm or indirect loss of leverage or by disease that results in osteopenia.
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code T148. Fracture of inferior orbital wall. The base of the skull is a complex structure that forms the floor of the cranial cavity and separates the brain from the head and neck.
Nasal packing should not be directed superiorly as patients with persistent bleeding may have associated nasoethmoid orbital fracture. Lateral orbital wall. This is indicated by inability to move the eye in upward gaze or sometimes downward gaze and one may observe autonomic instability the oculocardiac reflex.
Indirect orbital floor fracture. Aims and ScopeJPRAS An International Journal of Surgical Reconstruction is one of the worlds leading international journals covering all the reconstructive and aesthetic aspects of plastic surgeryThe journal presents the latest surgical procedures with audit and outcome studies of new and established techniques in plastic surgery including. CME Information and Guidelines for Manuscript Review.
Immediate first aid consists of splinting the bone with no attempt to. Facial trauma also called maxillofacial trauma is any physical trauma to the faceFacial trauma can involve soft tissue injuries such as burns lacerations and bruises or fractures of the facial bones such as nasal fractures and fractures of the jaw as well as trauma such as eye injuriesSymptoms are specific to the type of injury. Extraocular muscle entrapment from orbital floor fracture in a child.
Fracture of orbital floor. Such trauma can also affect the surrounding eye muscles making eye movement harder and more painful. The Editors of American Journal of Ophthalmology in conjunction with the Elsevier Office of Continuing Medical Education EOCME are pleased to offer an AMA PRA Category 1 CreditsTM credit program for registered American Journal of Ophthalmology physician reviewers reviewers who complete.
Orbital rim fractures typically result from car accidents and similar traumatic events. Refer for CT facial. In the spring of 2020 we the members of the editorial board of the American Journal of Surgery committed to using our collective voices to publicly address and call for action against racism and social injustices in our society.
Fractures involving more than one bone most commonly affect the orbital floor and zygomaticomaxillary complex 4. The mission of Urology the Gold Journal is to provide practical timely and relevant clinical and scientific information to physicians and researchers practicing the art of urology worldwide. The bony orbit of the dog and cat is incomplete.
It is composed of the temporal occipital sphenoid and ethmoid bones as well as the orbital part of the. Fractures of the orbital floor are common. CT is the mainstay of imaging of acute TBI for both initial triage and follow-up as it is fast and accurate in detecting both primary and secondary injuries that require.
The breaking of a part especially a bone. 17 Inadvertent penetration of the orbital floor during caudal maxillary tooth extraction is often multifactorial and may be associated with the regional anatomy. Concha bullosa refers to pneumatization of the middle turbinate.
A Haller cell represents an ethmoid air cell that is located lateral to the maxillo-ethmoidal suture along the medial orbital floor orbital surface of the maxillary bone which may result in narrowing of the maxillary antrum and proximal infundibulum. Complications of nasal injury. The British Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons BAOMS has produced specialty specific criteria standards and evidence for the practice of oral and maxillofacial surgery in the UK.
Anterior or lateral maxillary sinus wall or orbital floor. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry is the leading professional journal devoted exclusively to prosthetic and restorative dentistryThe Journal is the official publication for 24 leading US. Significant eye trauma can cause the orbital bone and surrounding structures to cave downward into the socket.
Other injury of unspecified body region. This is typically caused by a direct blow to the central orbit from a fist or ball. Performed to identify the exact location of the fracture and potential risk of complications.
This will usually occur as a result of severe trauma. Children with orbital fracture and oculomotor dysfunction tend to have a more favorable outcome if the repair is done within the first 7 days. This monthly journal offers comprehensive coverage of new techniques important developments and innovative ideas in oral and maxillofacial surgeryPractice-applicable articles help develop the methods used to handle dentoalveolar surgery facial injuries and deformities TMJ disorders oral cancer jaw reconstruction anesthesia and analgesiaThe journal also.
Orbital blowout fractures occur when there is a fracture of one of the walls of orbit but the orbital rim remains intact. For example fractures may involve pain. The concept of facial buttresses has also been.
The force of the blow pushes the eyeball further into the eye socket fracturing the very thin walls of bone that make up the eye socket. Relative indications for surgery are high-risk fractures for enophthalmos which involve over one-half of the orbital floor or lateral orbital wall. Epidemiology The blowout fracture is t.
An orbital rim fracture may extend to the orbital floor to cause a direct orbital floor fracture. The floor of the orbit is composed of soft tissues including the zygomatic salivary gland orbital fat and medial pterygoid muscle. Medial orbital wall.
Our mission is to elevate the quality and safety of healthcare worldwide through the advancement of patient care education and research furthering the art and science of oral and. To promote equity and diversity among authors reviewers and editors. Some surgeons report good results with an early repair.
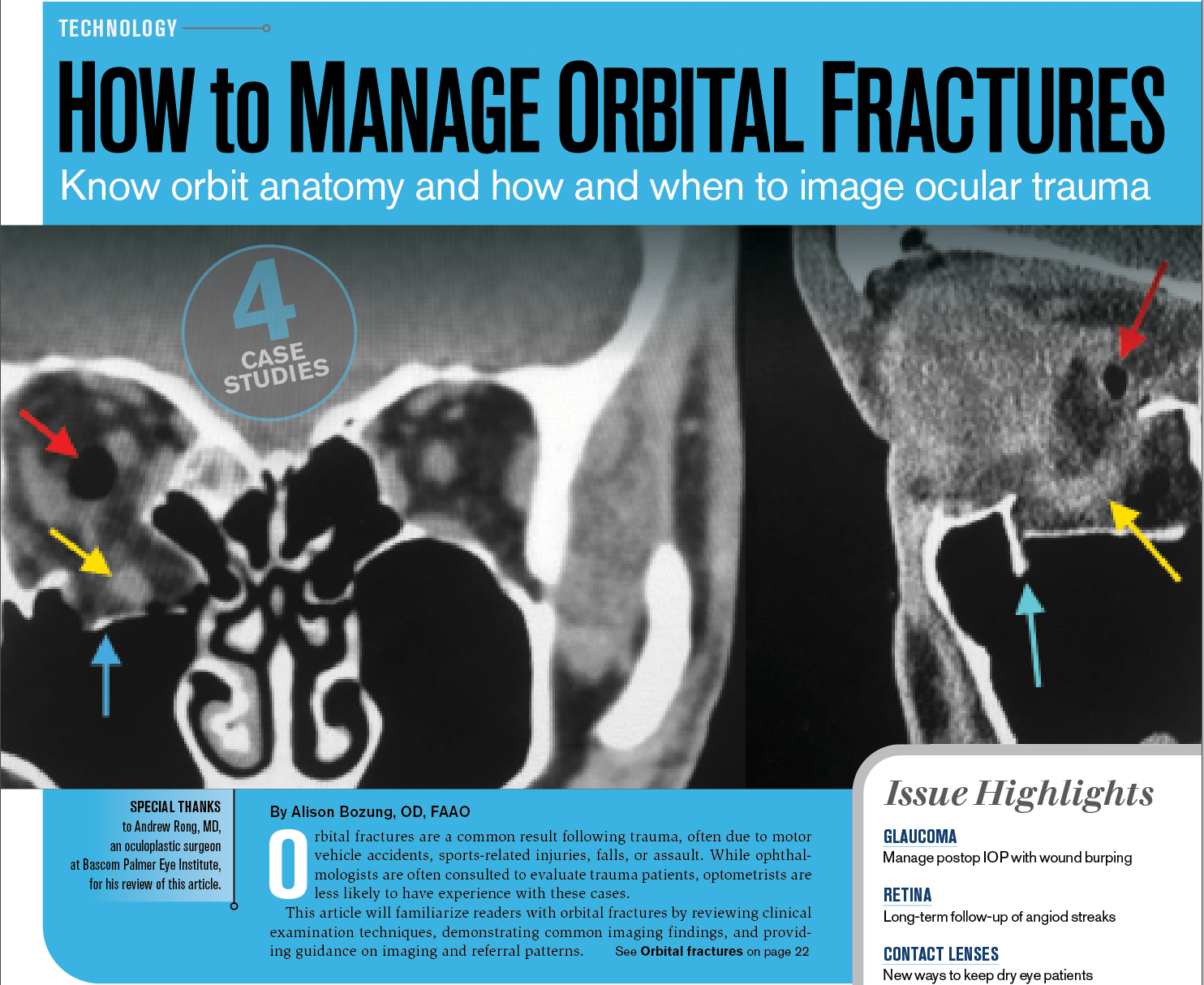
How To Manage Orbital Fractures

A Case Of Combined Orbital Floor And Medial Wall Fracture A 44 Year Old Download Scientific Diagram
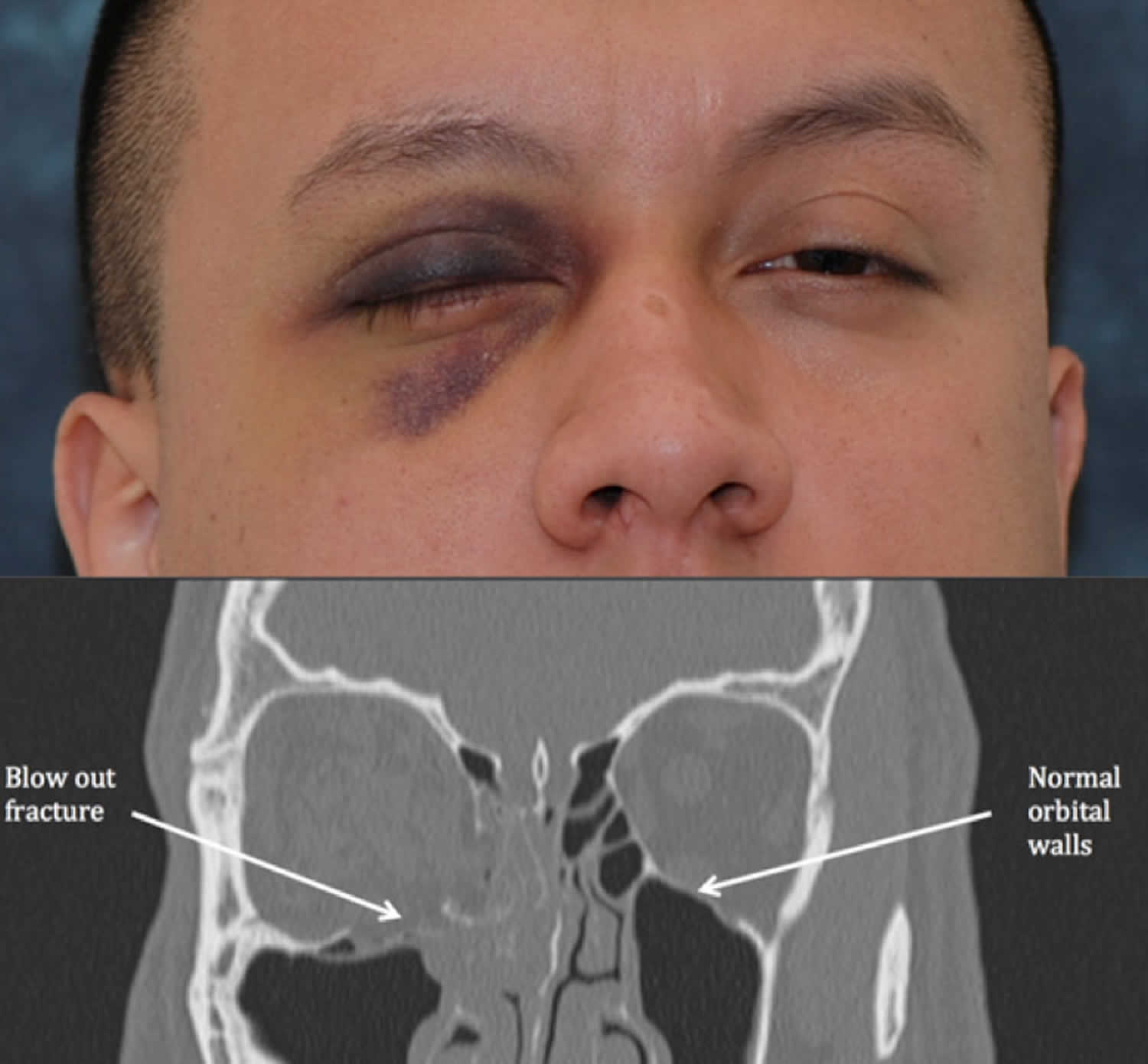
Orbital Floor Fracture Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis
Preseptal Transconjunctival Approach For Orbital Floor Fracture Repair And Associated Complications Indiana University
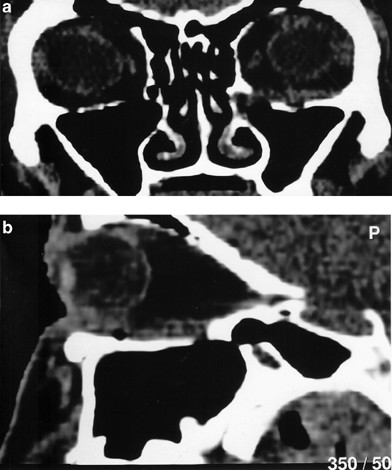
Orbital Floor Fracture An Unusual Late Complication Eye

Fractures Involving Bony Orbit A Comprehensive Review Of Relevant Clinical Anatomy Sciencedirect